使用 createContext 和 useContext 进行深度状态传递
更新: 11/20/2025字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
在 React 开发中,组件间的数据传递通常通过 props 实现。但当需要在多层组件间共享数据时,props 逐层传递会变得十分繁琐,这就是所谓的 "props drilling" 问题。为了避免这个问题, React 提供的解决方案:createContext 和 useContext。
什么是 React Context?
React Context 提供了一个在组件树中共享数据的方法,而无需在每个层级手动传递 props。它由三个核心部分组成:
- createContext - 创建 Context 对象
- Context.Provider - 提供数据的组件
- useContext - 消费数据的 Hook(也就是使用 Provider 传递的数据)
完整案例演示
让我们通过一个用户信息管理和主题切换的案例来深入理解这两个 API 的使用。
组件的源码放到文章的最后。
效果演示
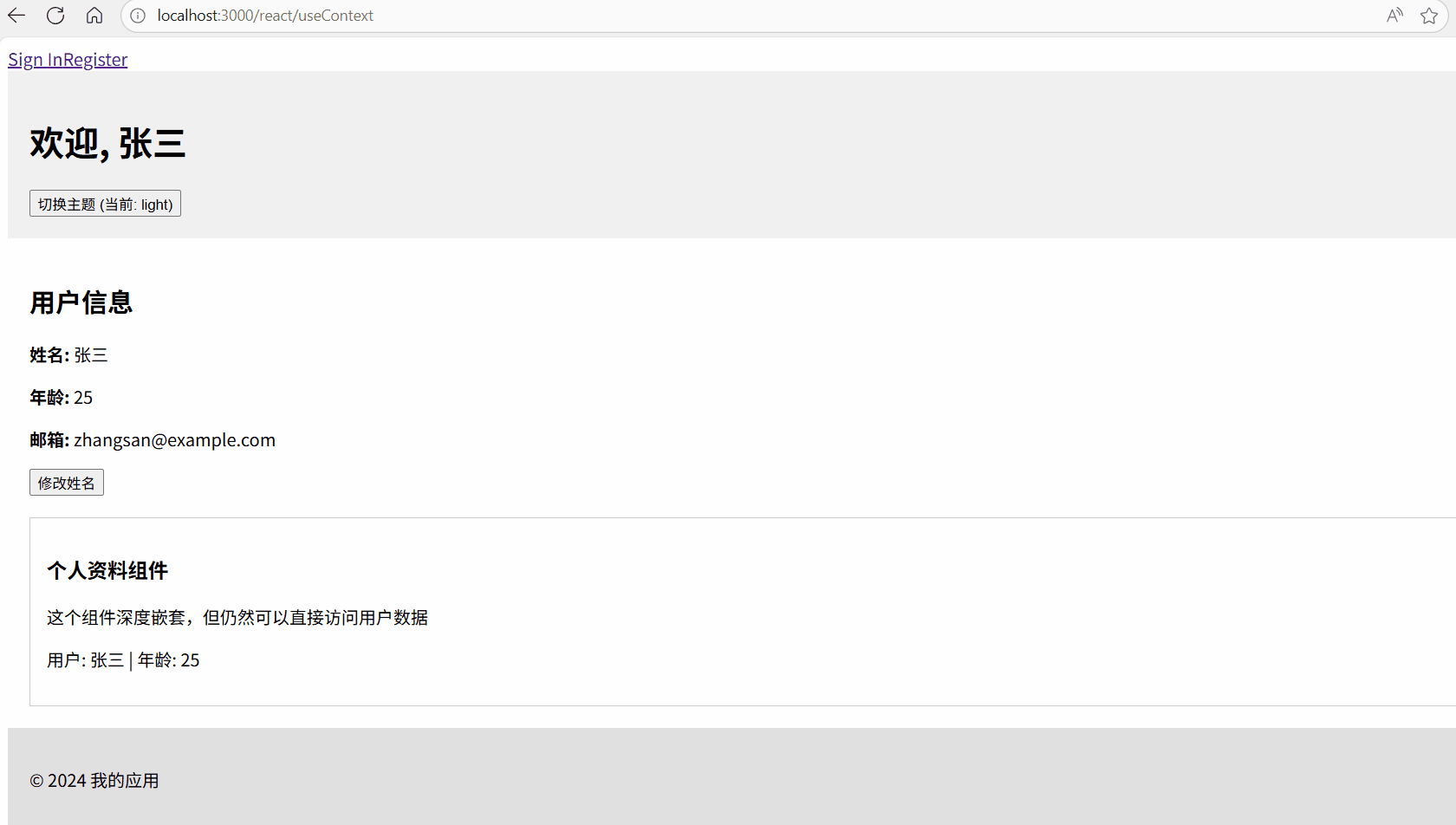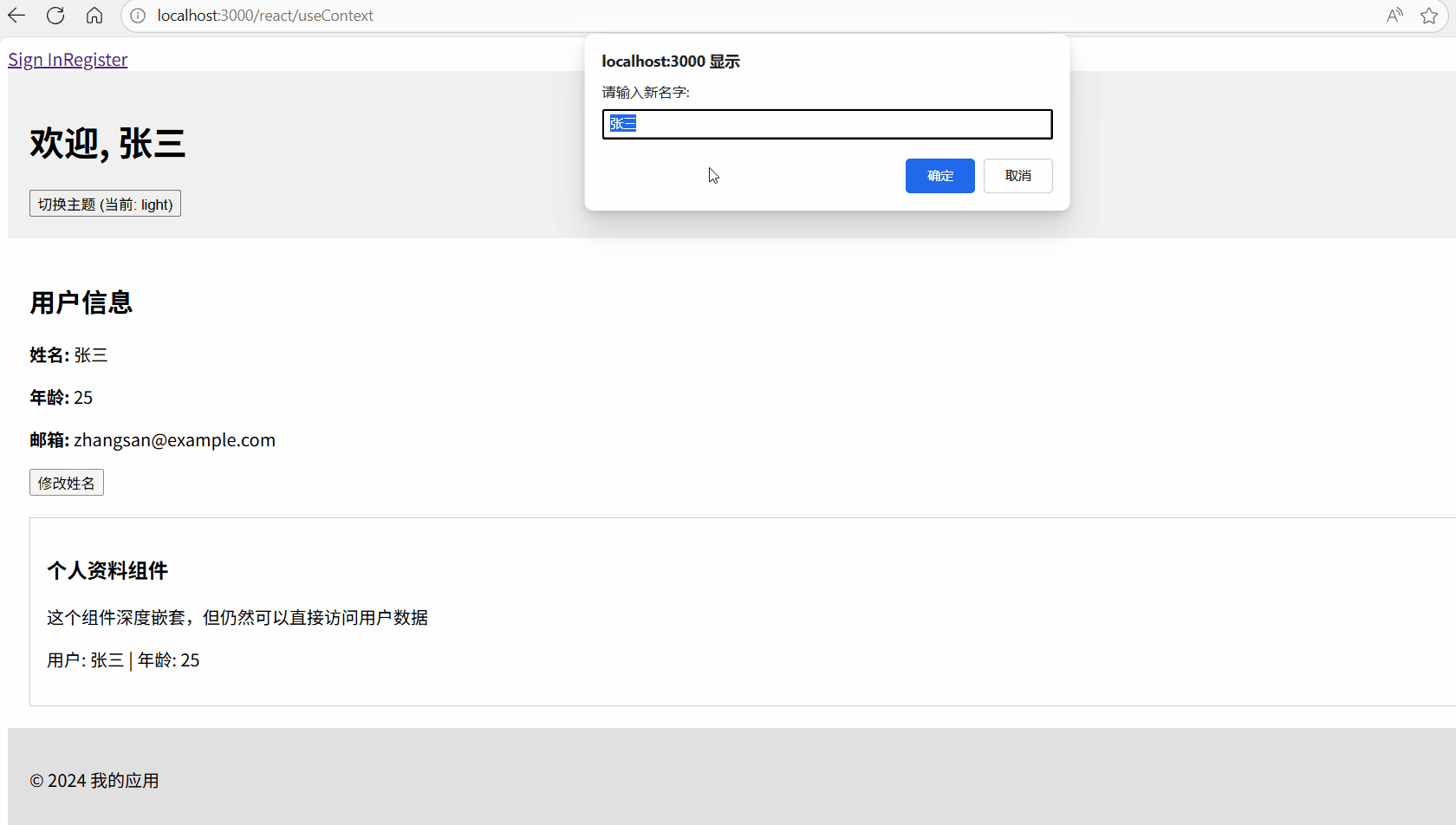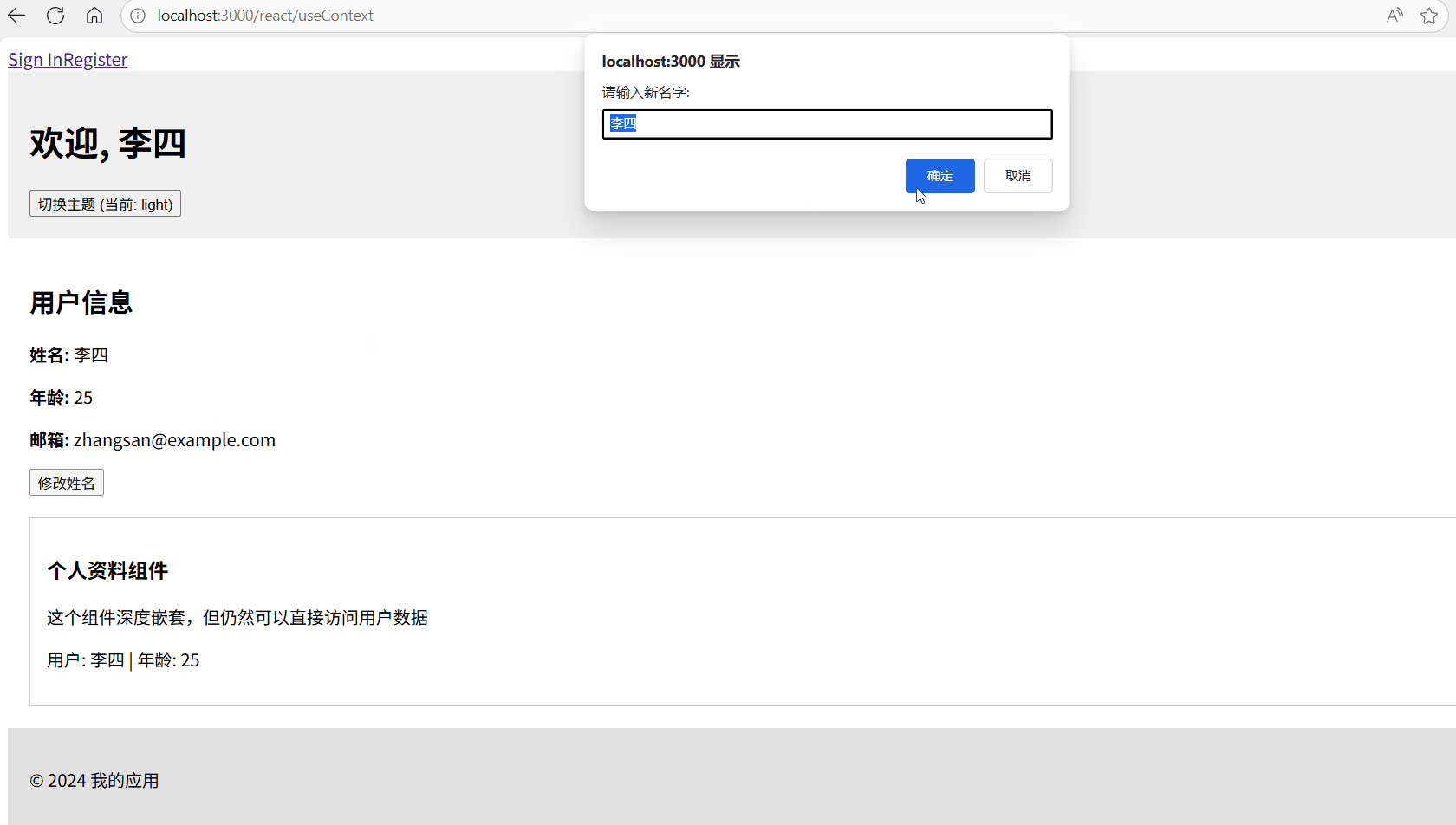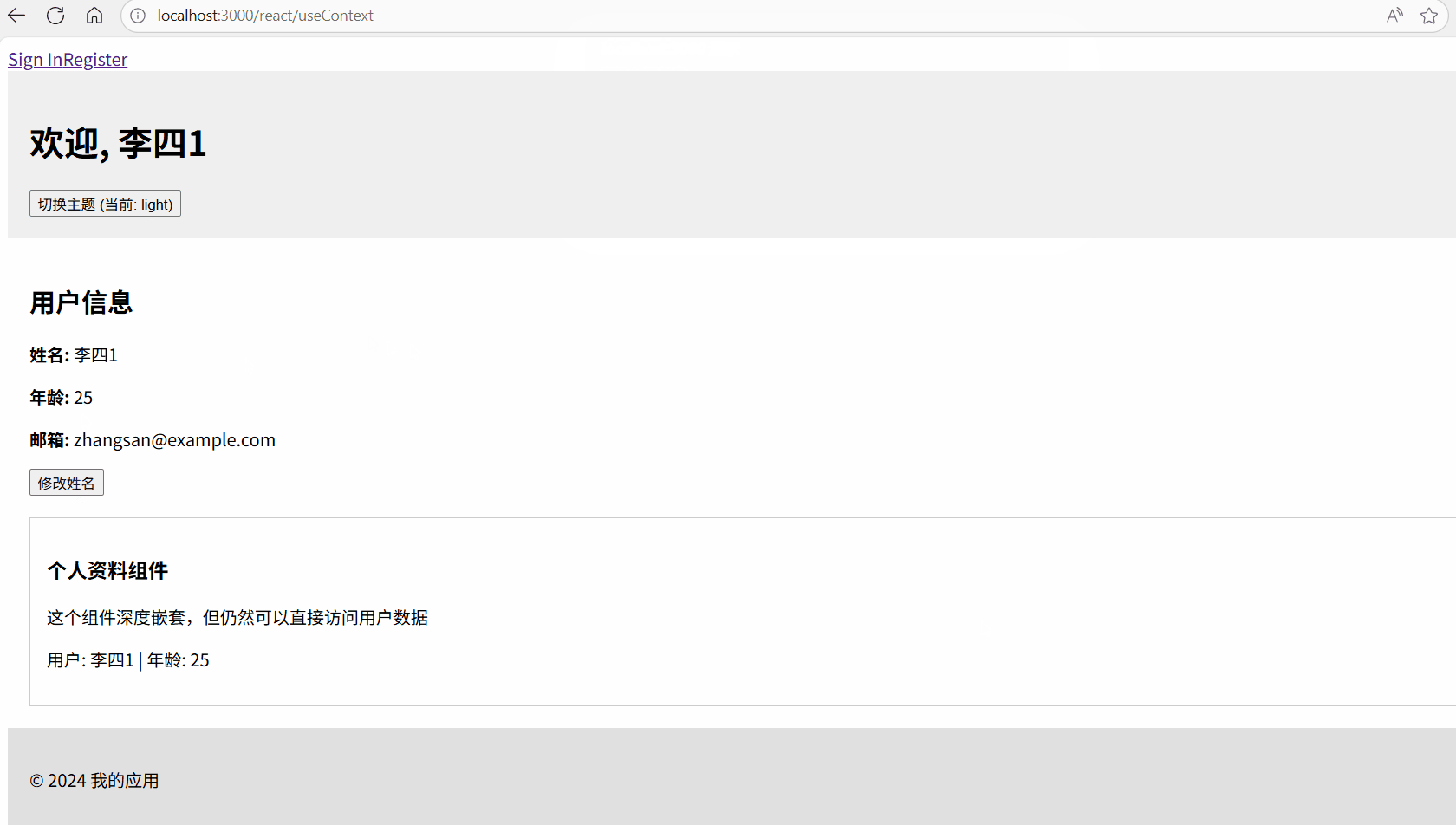
1. 创建 Context
首先,我们需要创建 Context 对象来定义要共享的数据结构:
jsx
import React, { createContext, useContext, useState } from "react";
// 创建用户相关的 Context
// 这个 Context 将包含用户信息和更新用户的方法
const UserContext = createContext();
// 创建主题相关的 Context
// 这个 Context 将包含主题信息和切换主题的方法
const ThemeContext = createContext();讲解:
createContext()创建一个 Context 对象- 可以创建多个 Context 来管理不同类型的状态
- 每个 Context 都是独立的数据流
2. 实现 Provider 组件
Provider 组件是数据的提供者,它包裹需要访问这些数据的子组件:
jsx
function App() {
// 用户状态管理
const [user, setUser] = useState({
name: "张三",
age: 25,
email: "zhangsan@example.com"
});
// 主题状态管理
const [theme, setTheme] = useState("light");
// 切换主题的函数
const toggleTheme = () => {
setTheme((prevTheme) => (prevTheme === "light" ? "dark" : "light"));
};
// 更新用户信息的函数
const updateUser = (newUserData) => {
setUser((prevUser) => ({ ...prevUser, ...newUserData }));
};
return (
// UserContext.Provider 提供用户相关数据
// value 属性包含所有要共享的数据和方法
<UserContext.Provider value={{ user, updateUser }}>
{/* ThemeContext.Provider 提供主题相关数据 */}
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{ theme, toggleTheme }}>
{/* 应用容器,根据当前主题设置样式 */}
<div className={`app ${theme}`}>
<Header />
<MainContent />
<Footer />
</div>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</UserContext.Provider>
);
}关键点:
- Provider 组件通过
value属性传递数据 - 多个 Provider 可以嵌套使用
- 当
value变化时,所有消费该 Context 的组件都会重新渲染
3. 消费 Context 的组件
现在让我们看看如何在各个组件中使用这些共享数据:
Header 组件
jsx
function Header() {
// 使用 useContext 获取 UserContext 的值
// 这里我们获取用户信息和主题切换功能
const { user } = useContext(UserContext);
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<header
style={{
padding: "20px",
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#f0f0f0" : "#333",
color: theme === "light" ? "#000" : "#fff"
}}
>
<h1>欢迎, {user.name}</h1>
{/* 直接使用 toggleTheme 函数,无需通过 props 传递 */}
<button onClick={toggleTheme}>切换主题 (当前: {theme})</button>
</header>
);
}MainContent 组件
jsx
function MainContent() {
// 获取用户信息和更新用户的方法
const { user, updateUser } = useContext(UserContext);
const handleNameChange = () => {
const newName = prompt("请输入新名字:", user.name);
if (newName) {
// 直接调用 Context 中提供的方法更新状态
updateUser({ name: newName });
}
};
return (
<main style={{ padding: "20px" }}>
<h2>用户信息</h2>
<div>
<p>
<strong>姓名:</strong> {user.name}
</p>
<p>
<strong>年龄:</strong> {user.age}
</p>
<p>
<strong>邮箱:</strong> {user.email}
</p>
</div>
<button onClick={handleNameChange}>修改姓名</button>
{/* Profile 组件可以直接访问 Context,无需通过 props 传递数据 */}
<Profile />
</main>
);
}Profile 组件 - 深层嵌套示例
jsx
function Profile() {
// 在深层嵌套组件中直接使用 Context
// 无需通过 MainContent 组件逐层传递 props
const { user } = useContext(UserContext);
const { theme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<div
style={{
marginTop: "20px",
padding: "15px",
border: `1px solid ${theme === "light" ? "#ccc" : "#666"}`,
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#fff" : "#444"
}}
>
<h3>个人资料组件</h3>
<p>这个组件深度嵌套,但仍然可以直接访问用户数据</p>
<p>
用户: {user.name} | 年龄: {user.age}
</p>
</div>
);
}Footer 组件
jsx
function Footer() {
// 只使用主题信息
const { theme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<footer
style={{
padding: "20px",
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#e0e0e0" : "#222",
color: theme === "light" ? "#000" : "#fff"
}}
>
<p>© 2024 我的应用</p>
</footer>
);
}核心概念解析
1. createContext 的工作原理
jsx
const MyContext = createContext(defaultValue);defaultValue仅在组件未匹配到 Provider 时使用- 创建的 Context 对象包含
Provider和Consumer组件
2. useContext 的机制
jsx
const value = useContext(MyContext);- 接受一个 Context 对象并返回该 Context 的当前值
- 当前值由上层组件中距离当前组件最近的
Provider的valueprop 决定 - 当 Provider 更新时,使用该 Context 的 Hook 会触发重渲染
3. Provider 的价值传递
jsx
<MyContext.Provider value={/* 某个值 */}>valueprop 可以是任何类型:对象、数组、函数等- 建议将相关状态和方法组合成一个对象传递
- 避免创建不同的 Provider 来传递单个值
最佳实践
1. 性能优化
当传递对象作为 value 时,使用 useMemo 避免不必要的重渲染:
jsx
const value = useMemo(() => ({ user, updateUser }), [user]);
return <UserContext.Provider value={value}>{children}</UserContext.Provider>;2. 自定义 Hook 模式
jsx
function useUser() {
const context = useContext(UserContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error("useUser must be used within a UserProvider");
}
return context;
}3. 多 Context 组合
对于复杂的应用,可以创建多个特定的 Context 而不是一个庞大的 Context:
jsx
// 好的做法:分离关注点
<UserContext.Provider>
<ThemeContext.Provider>
<AuthContext.Provider>{children}</AuthContext.Provider>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</UserContext.Provider>使用场景
- 主题切换 - 如本文案例所示
- 用户认证 - 用户登录状态、权限信息
- 多语言国际化 - 当前语言设置
- 全局状态管理 - 购物车、用户偏好设置等
案例源码
tsx
"use client";
import React, { createContext, useContext, useState } from "react";
// 1. 创建 用户信息的 Context
const UserContext = createContext({
user: {
name: "张三",
age: 25,
email: "zhangsan@example.com"
},
updateUser: (newUserData: object) => {}
});
// 1. 创建 主题的 Context
const ThemeContext = createContext({
theme: "light",
toggleTheme: () => {}
});
// 2. 提供 Context 的组件 (Provider)
function App() {
const [user, setUser] = useState({
name: "张三",
age: 25,
email: "zhangsan@example.com"
});
const [theme, setTheme] = useState("light");
const toggleTheme = () => {
setTheme((prevTheme) => (prevTheme === "light" ? "dark" : "light"));
};
const updateUser = (newUserData: object) => {
setUser((prevUser) => ({ ...prevUser, ...newUserData }));
};
return (
// 提供 UserContext
<UserContext.Provider value={{ user, updateUser }}>
{/* 提供 ThemeContext */}
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{ theme, toggleTheme }}>
<div className={`app ${theme}`}>
{/* 这里Header和MainContent、Footer都能获取 user 和 theme */}
<Header />
<MainContent />
<Footer />
</div>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</UserContext.Provider>
);
}
// 3. 使用 Context 的组件
function Header() {
// 使用 useContext 获取 UserContext 的值
const { user } = useContext(UserContext);
const { theme, toggleTheme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<header
style={{
padding: "20px",
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#f0f0f0" : "#333",
color: theme === "light" ? "#000" : "#fff"
}}
>
<h1>欢迎, {user.name}</h1>
<button onClick={toggleTheme}>切换主题 (当前: {theme})</button>
</header>
);
}
// 主要内容
function MainContent() {
const { user, updateUser } = useContext(UserContext);
const handleNameChange = () => {
const newName = prompt("请输入新名字:", user.name);
if (newName) {
updateUser({ name: newName });
}
};
return (
<main style={{ padding: "20px" }}>
<h2>用户信息</h2>
<div>
<p>
<strong>姓名:</strong> {user.name}
</p>
<p>
<strong>年龄:</strong> {user.age}
</p>
<p>
<strong>邮箱:</strong> {user.email}
</p>
</div>
<button onClick={handleNameChange}>修改姓名</button>
<Profile />
</main>
);
}
// 更加深的组件
function Profile() {
// 在深层嵌套组件中直接使用 Context,无需逐层传递 props
const { user } = useContext(UserContext);
const { theme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<div
style={{
marginTop: "20px",
padding: "15px",
border: `1px solid ${theme === "light" ? "#ccc" : "#666"}`,
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#fff" : "#444"
}}
>
<h3>个人资料组件</h3>
<p>这个组件深度嵌套,但仍然可以直接访问用户数据</p>
<p>
用户: {user.name} | 年龄: {user.age}
</p>
</div>
);
}
// 页脚
function Footer() {
const { theme } = useContext(ThemeContext);
return (
<footer
style={{
padding: "20px",
backgroundColor: theme === "light" ? "#e0e0e0" : "#222",
color: theme === "light" ? "#000" : "#fff"
}}
>
<p>© 2024 我的应用</p>
</footer>
);
}
export default App;